Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
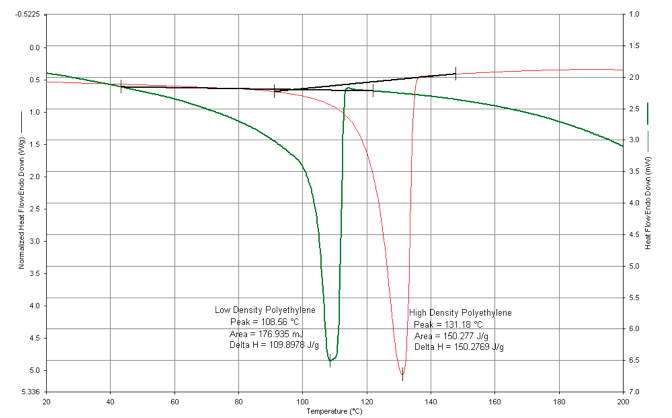
(Heat flow profiles as a function of either temperature or time)
What Is It?
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) is an analytical technique which measures the heat flow into or out of a sample as a function of time and/or temperature.
Why Should I Use It?
Temperature scanning profiles are created which subject the sample to changes in temperature, possibly along with one or more points where the sample is allowed to ‘soak’ at a fixed temperature.
What Do I Get Out of It?
Plots showing differences in heat flow between a sample and reference, as a function of time or temperature, yield information on thermal transitions in a sample due to melting, crystallization, chemical reactions, glass transitions, and other exothermic (heat evolving) and endothermic (heat absorbing) transitions.
Applications Include:
Polymers
- Identification
- Melt Point
- Glass Transition PointGlass Transition Point
- Degree of Crystallization
- Cross-Linking Characterization
Composites
- Characterization of Blends
- Examination of Epoxy Cure
Organic Additives
- Oxidative Stability of Antioxidant Formulations
- Heat Capacity
- Purity
Quality Control
- Cure quality of epoxies and epoxy composites
- Crystallization in pharmaceutical compounds
- Melting point depression
